In Java, there are two types of datatypes:
- Primitive data type
- Non-Primitive data type
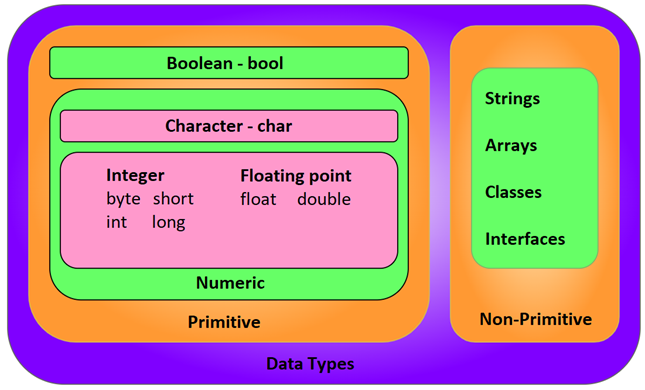
- The Boolean data type consists of two values, true and false.
- The char data type is used to store characters.
- The byte data type is used to conserve memory, and its values range from -128 to 127.
- The short data type consists of values ranging from -32768 to 32767, while the int data type consists of values ranging from -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647.
- The long data type consists of values ranging from -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807.
- The float data type is used to handle decimal numbers and is recommended over the double data type due to its memory-saving capabilities.
- The double data type is also used to handle decimal numbers.
