ABSTRACT:
Laser Communication System works on the principle of “Amplitude Modulation” process. In this the amplitude of the carrier is varied according to the instantaneous amplitude of the modulating signal (Input Signal ).
Here,
“Carrier Signal refers to Laser Beam”
“Amplitude refers to Intensity of Laser Beam”
“Input Signal refers to audio signal”
Hence, The intensity of the laser beam is varied according to the instantaneous value of audio signal and the same is sensed by the optical sensor at the receiver.
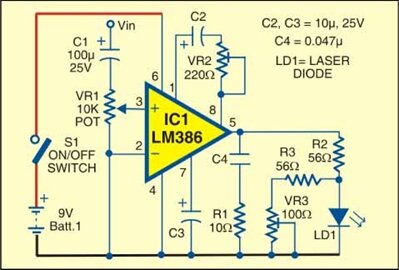
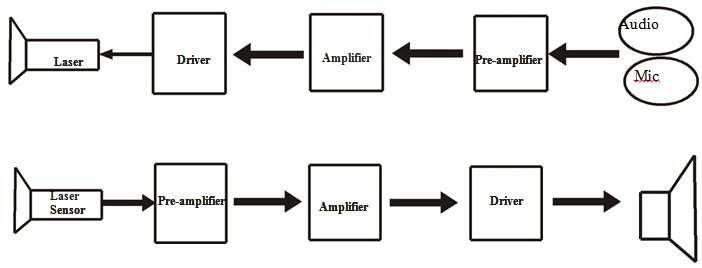
This simple Laser Communication System consists of two sections Transmitter and Receiver. At the Transmitter any audio device can be coupled to the laser light by using a transistor operating in common collector mode. Since, In common collector mode transistor acts as Impedence matching device. Due to this intensity of the laser beam changes proportional to audio signal strength.
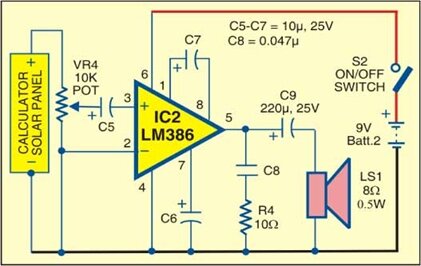
At the receiver this varying intensity can be sensed by any optical sensors like Light Dependent Resistor (LDR) or photo transistor or Solar cell. The photo transistor is biased and connected to the input of audio amplifier (LM386) which drives the loud speaker.
INTRODUCTION:
Lasers have been considered for space communications since their realization in 1960. Specific advancements were needed in component performance and system engineering particularly for space qualified hardware. Advances in system architecture, data formatting and component technology over the past three decades have made laser communications in space not only viable but also an attractive approach into inter satellite link applications.
Information transfer is driving the requirements to higher data rates, laser cross -link technology explosions, global development activity, increased hardware, and design maturity. Most important in space laser communications has been the development of a reliable, high power, single mode laser diode as a directly modulable laser source. This technology advance offers the space laser communication system designer the flexibility to design very lightweight, high bandwidth, low-cost communication payloads for satellites whose launch costs are a very strong function of launch weigh. This feature substantially reduces blockage of fields of view of most desirable areas on satellites. The smaller antennas with diameter typically less than 30 centimeters create less momentum disturbance to any sensitive satellite sensors. Fewer on board consumables are required over the long lifetime because there are fewer disturbances to the satellite compared with heavier and larger RF systems.
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
(a) TRANSMITTER
(b) RECEIVER
BLOCK DIAGRAM
PCB LAYOUT OF RECEIVER
PCB LAYOUT OF TRANSMITTER
it really helps to understand the concept of laser communication system
laser communication ppt
very nice… thank you so much for helping us…
Its really helps to understand the concept of laser communication system . .
Thank you so much…its very good
hello arishma. did u made any project on this? could u please help mee 4 this.