
Here is a simple IR sensor-based security system which will detect any movement and triger an alarm. This circuit is ideal for use in houses, banks, stores, and other restricted areas where a movement-based alert alarm is required. This circuit is based on an IR sensor in which an IR beam is continuously falling on a photodiode, and an alarm is activated anytime this Infrared beam is broken by any form of movement.
The circuit schematic is shown below.
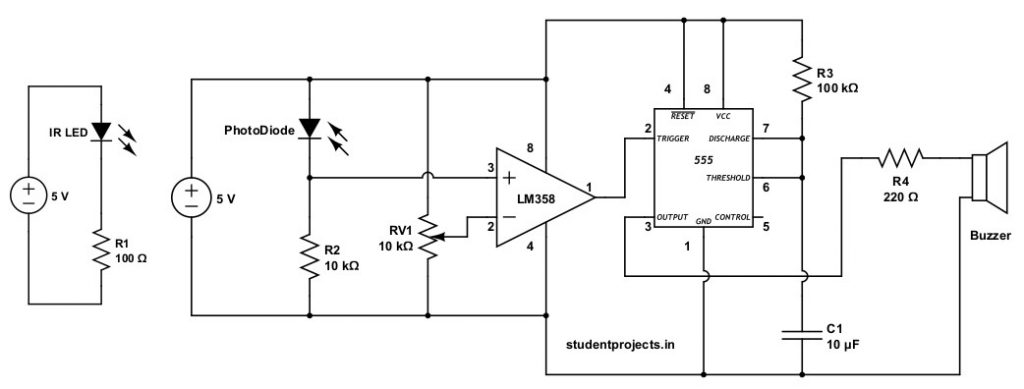
This security burgler alarm circuit is simple to build and only requires a few components, which are mentioned below.





IR LED
An IR LED (infrared light-emitting diode) is a special-purpose LED that emits infrared rays with wavelengths ranging from 700 nm to 1 mm. So it is invisible to human eyes. IR LEDs are more commonly used in security systems and remote control devices.
Photodiode
A photodiode is a semiconductor device with a P-N junction that converts light into an electrical current. The resistance and output voltage of the photodiode alter in response to the amount of infrared light received.
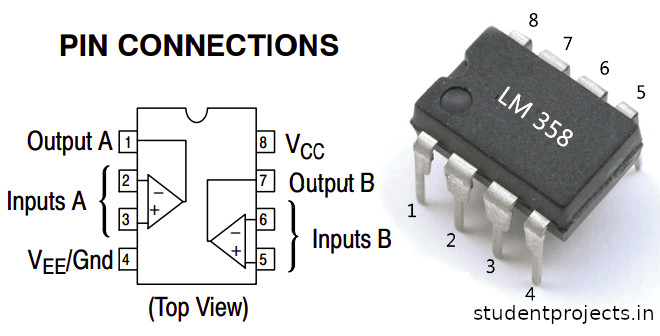
LM358
The LM358 is an operational amplifier (Op-Amp), and it is used as a voltage comparator in this design. The LM358 contains two independent voltage comparators. We have used only one comparator, with inputs at PINs 2 and 3 and outputs at PIN 1. The voltage comparator has two inputs: one inverting and the other non-inverting (PIN 2 and 3). The output of the comparator (PIN 1) is High when the voltage at the non-inverting input (+) is greater than the voltage at the inverting input (-). If the inverting input (-) has a higher voltage than the non-inverting end (+), the output is LOW.
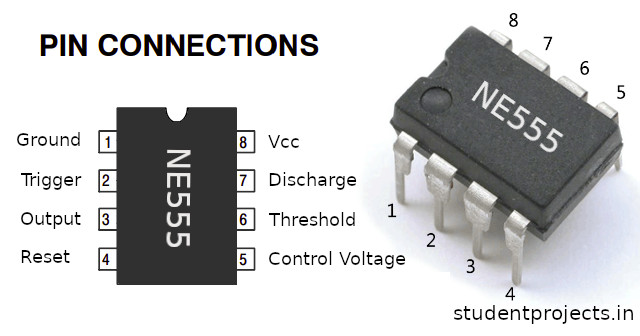
NE555
The 555 Timer is is configured as a monostable mode in this example. When a falling edge is detected on pin 2(trigger pin), the output voltage rises high for a predetermined duration.
Working of an IR Sensor
An IR LED serves as the emitter, while an IR photodiode serves as the detector. An IR LED emits infrared light, which is detected by the IR photodiode. The resistance and output voltage of the photodiode alter in response to the amount of infrared light received. In this circuit we will detect when there is no light falling on the photodiode and trigger an alarm.
How does the IR based burgler alarm circuit work?
As per the circuit diagram given above, a variable resistor is connected to inverting end of LM358(Pin 2) to adjust the sensitivity of the sensor. A junction of the photodiode and a resistor is connected to the non-inverting end of LM358(Pin 3). LM358 op-amp voltage comparator’s output (PIN1) is connected to the 555 timer’s Trigger pin. The 555 Timer is set to monostable mode in this example.
When the circuit is switched ON and when there is IR radiation towards the photodiode, the voltage across it drops, while the voltage across the series resistor R2 increases. Non-inverting end (pin 3) gets high voltage when compared to inverting end (pin2). Hence the output of the comparator is HIGH, because the comparator output is connected to the 555 timer’s trigger pin, the 555 output is low when Trigger pin 2 is high. As a result, the 555 timer output remains LOW when the IR rays fall on the Photodiode. Read this article to learn how the IR sensor works with the LM358 comparator.
Now when the IR radiation towards the photodiode breaks due to some movement, the voltage across it increases, while the voltage across the series resistor R2 decreases. Non-inverting end (+) gets low voltage when compared to inverting end (-). Hence the output of the comparator is LOW, because the comparator output is connected to the 555 timer’s trigger pin, the 555 output is HIGH when Trigger pin 2 is low. As a result, the 555 timer output becomes HIGH and the he buzzer beeps for a short time. By altering the value of resistor R1 or capacitor C1, the duration of the beep can be lengthened.
Inverting end of LM358 is connected to the 10k pot. Make the necessary adjustments to ensure that voltage comparison works properly.
So, give it a shot and let me know if you have any questions in the comments section below. I’ll be happy to assist you!
