A supply chain is a network that connects a firm with its suppliers in order to manufacture and deliver a certain product to the final consumer.
This network consists of many activities, individuals, entities, data, and information resources. The supply chain also depicts the steps required to obtain a product or service to the consumer in its original state.
A supply chain is a set of procedures for getting a product or service to a consumer. Moving and processing raw materials into finished products, transporting those items, and distributing them to final users are all processes in the process. Producers, vendors, warehouses, transportation companies, distribution hubs, and retailers are all part of the supply chain. The functions of a supply chain start with receiving an order and end with fulfilling the customer’s request. Product creation, marketing, operations, distribution networks, financing, and customer service are among these functions.
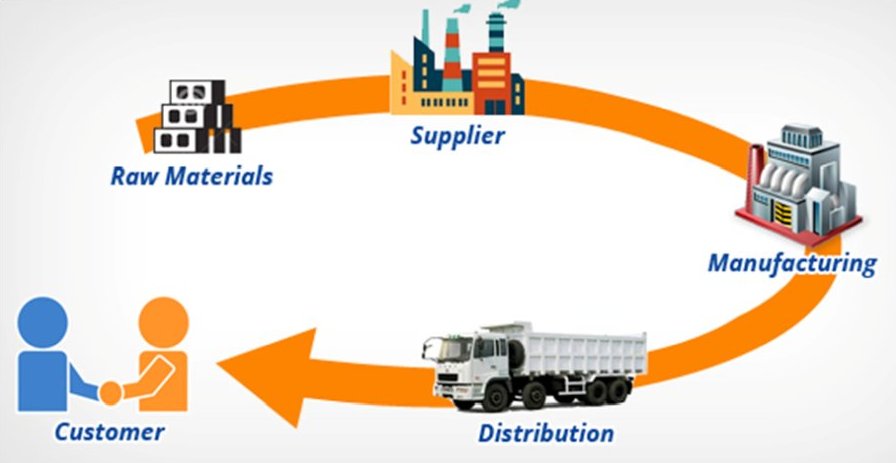
A simple supply chain is made up of various components that are connected through product movement. The customer is at the beginning and end of the supply chain.
- Customer: When a buyer decides to buy a product that has been offered for sale by a corporation, they begin the chain of events. The customer contacts the company’s sales department, which places a sales order for a specified quantity to be delivered on a certain date. If the product must be made, the sales order will include a criteria that the manufacturing facility must meet.
- Planning: The customer’s sales order will trigger a requirement that will be merged with other orders. The planning department will establish a production plan to manufacture the products in order to satisfy the demands of the customers. The corporation will then have to obtain the raw materials required to make the products.
- Purchasing: The purchasing department receives a list of raw materials and services that the manufacturing department requires in order to fulfil the customer’s orders. The purchasing department issues purchase orders to selected suppliers, instructing them to deliver the required raw materials to the manufacturing facility on time.
- Inventory: Raw materials are received from suppliers, examined for quality and accuracy, and then placed in the warehouse. The supplier will subsequently send the company an invoice for the items delivered. The raw materials are kept in storage until the production department needs them.
- Production: Raw materials are relocated inventory to the production area according to a manufacturing plan. The finished items that the consumer orders are made from raw materials obtained from vendors. After the items have been finished and tested, they are returned to the warehouse for storage before being delivered to the customer.
- Transportation: When the finished product arrives in the warehouse, the shipping department chooses the most effective shipping option to ensure that the products are delivered on or before the customer’s deadline. The organisation will send an invoice for the delivered products once the goods have been received by the customer.
Supply chain management (SCM) is the discipline that oversees supplies and processes throughout the life cycle of a project, product, or service. The journey of business content takes it from one state to the next until it’s ready to be given to the consumer or stakeholder. The logistics of transporting the finished product from one location to another are also involved. Control is required to move through these many stages efficiently, which is where supply chain management comes in.
