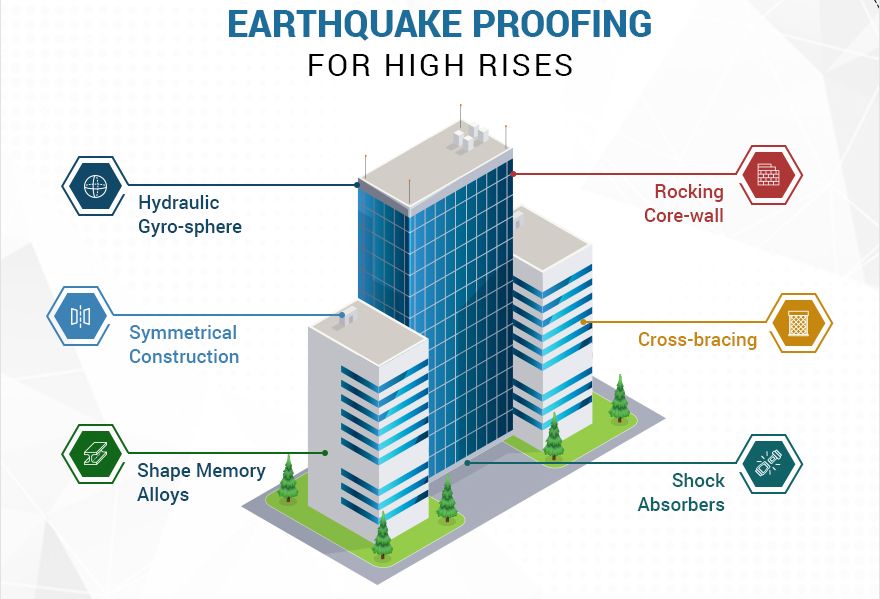
The seismic forces exerted on a building are not externally developed forces like wind instead they are the response of cyclic motions at the base of a building causing accelerations and hence inertia force. The response is therefore essentially dynamic in nature.
The dynamic properties of the structure such as natural period, damping and mode shape
play a crucial role in determining the response of the building. Besides other characteristics of the building system also affect the seismic response such as ductility, building foundation, the response of non-structural elements etc.

Mode Shapes and Fundamental Period:
- The elastic properties and mass of building cause to develop a vibratory motion when they are subjected to dynamic action.
- This vibration is similar to vibration of a violin string, which consists of a fundamental tone and the additional contribution of various harmonics.
- The vibration of a building likewise consists of a fundamental mode of vibration and the additional contribution of various modes, which vibrates at higher frequencies.
- Fundamental period of vibration can be determined by the code-based empirical for the fundamental modes of the building may be determined by any one of several methods developed for the dynamic analysis of structures.
- On the basis of time period, building may be classified as rigid (T<T 1.0 sec).
- Buildings with higher natural frequencies, and a short natural period, tend to suffer higher accelerations but smaller displacement.
- In the case of buildings with lower natural frequencies, and a long natural period, this is reversed: the buildings will experience lower accelerations but larger displacements.

Building Frequency and Ground Period:
- Inertial forces generated in the building depend upon the frequencies of the ground on which the building is standing and the building’s natural frequency
- When these are near or equal to one another, the building’s response reaches a peak level.
- Past studies show that the predominant period at a firm ground site 0.2-0.4 sec rigid structures (0-0.3) will have more unfavourable seismic response than flexible structures ,while period on soft ground can reach 2.0 sec or more.
- Seismic response of flexible structures (t>1.0) on soft foundation sites will be less favourable than that of rigid structure.
- Building fundamental periods of approximately 0.1N (where, N is the number of storey)
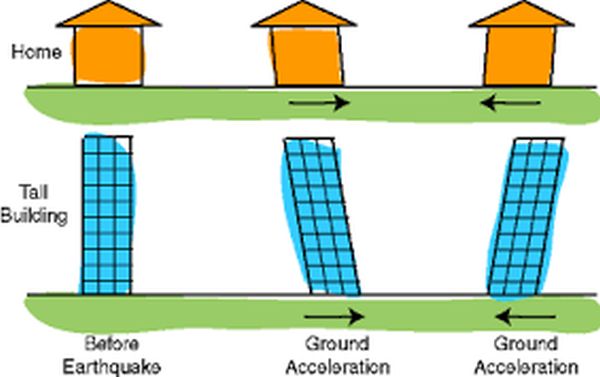
Damping:
- The degree of structural amplification of the ground motion at the base of the building is limited by structural damping.
- Damping is the ability of the structural system to dissipate the energy of the earthquake ground shaking.
- Since the building response in inversely proportional to damping in a building possesses, the sooner it will stop vibrating–which of course is highly desirable from the standpoint of earthquake performance.
- In a structure, damping is due to internal friction and the absorption of energy by the building’s structural and non-structural elements.
- There is no numerical method available for determining the damping. It is only obtained by experiments.
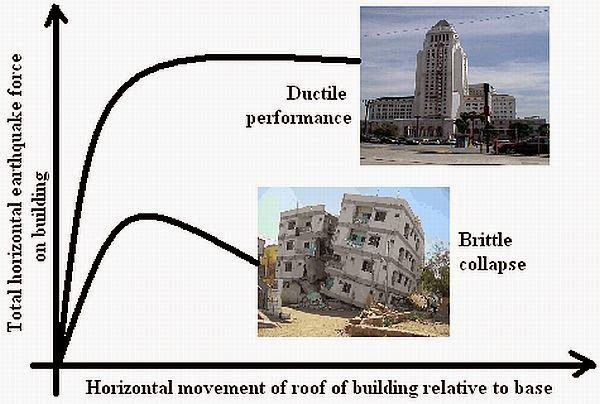
Ductility:
- Ductility is defined as the capacity of the building materials, systems, or structures to energy by deforming in the inelastic range.
- The safety of building from collapse is on the basis of energy, which must be imparted to the structure in order to make it fail. In such instance, consideration must be given to structure’s capacity to absorb energy rather than to its resistance.
- Therefore ductility of a structure in fact is one of the most important factors affecting its earthquake performance.
- The primary task of an engineer designing a building to be earthquake resistant is to ensure that the building will possess enough ductility.
- The ductility of a structure depends on the type of material used and also the structural assembly.
Seismic Weight:
- Seismic forces are proportional to the building weight and increases along the height of building.
- Weight reduction can be obtained by using lighter materials or by reducing the filling and other heavy equipment’s not essential for building construction.

Quality of Construction and Materials:
- Grade of concrete not achieved in site – reasons.
- Poor execution of the concrete joint/ discontinuity-quality of concrete
- Reinforcement detailing not taken care of appropriately.
- Accumulation of sawdust, dust and loose materials at the surface of joint.
- Result: A defective concrete joint, which contributed significantly to causing of failure of many building in past earthquakes.