The production of high-quality concrete necessitates painstaking attention to detail at every stage of the process.
It’s worth noting that the elements in both good and bad concrete are the same.
The final concrete will be of poor quality if diligent attention is not exercised and good regulations are not followed.
With the same material, if great care is used to maintain control at every stage, good concrete will result.
As a result, we must understand what are the best practices to follow at each stage of the concrete manufacturing process in order to produce high-quality concrete.
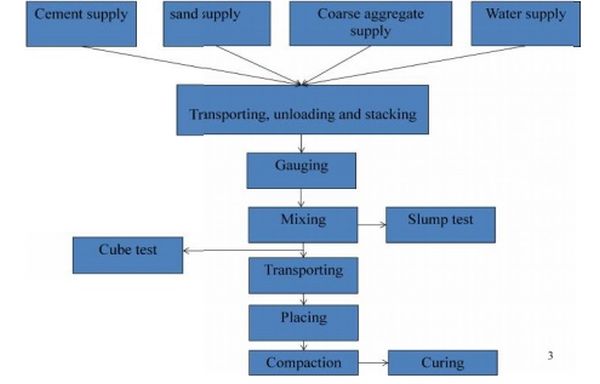
The various stages of manufacture of concrete are:
- Batching
- Mixing
- Transporting
- Placing
- Compacting
- Curing
1. BATCHING
Batching of concrete is the process of measuring ingredients or supplies in order to make a concrete mix. To obtain a high-quality concrete mix, proper batching is required.
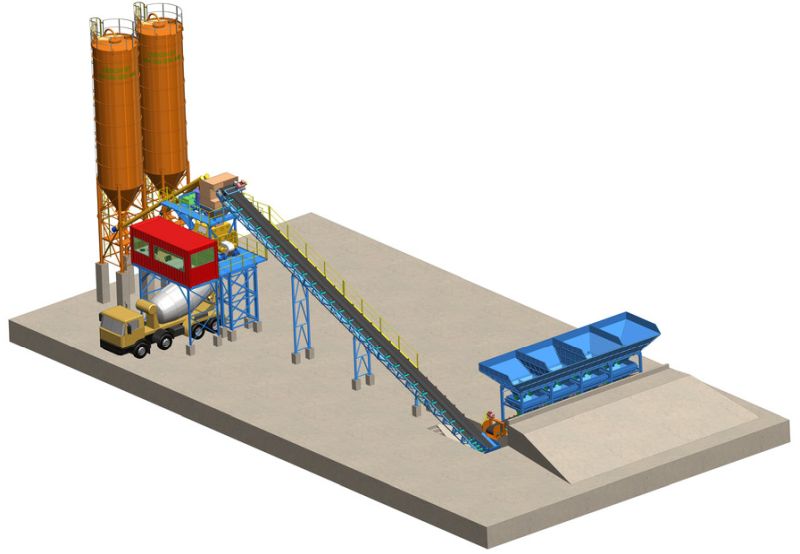

There are two methods for batching:
1.1 Volume batching:
Materials are measured on the basis of volume in volume batching. It is a less exact batching method. Materials are measured using measurement boxes or gauge boxes of known volume. Cement is packaged in bags, with a volume of 35 litres for each bag of cement (50 kilogrammes). The volume of the gauge box is set to the volume of one bag of cement (35 litres) or a multiple thereof. To make a 1:1:2 ratio concrete mix according to volume batching, one should take one bag of cement (35 litres), 1 gauge box of fine aggregate (35 litres) and 2 gauge boxes of fine aggregate (70 litres). If the water-cement ratio is 0.5, then half of the volume of cement which is 25 litres of water should be taken.
1.2 Weigh batching:
Weigh batching is the correct way of measuring the ingredients strictly speaking. Weigh batching systems should always be used for essential concrete. The use of a weight system in batching improves accuracy, flexibility, and ease of use.

2. MIXING
For the manufacture of homogenous concrete, thorough mixing of the materials is required.
The mixing process should result in a homogenous, colour- and consistency-uniform mass.
Concrete is mixed using one of two methods:
- Machine Mixing
- Hand mixing
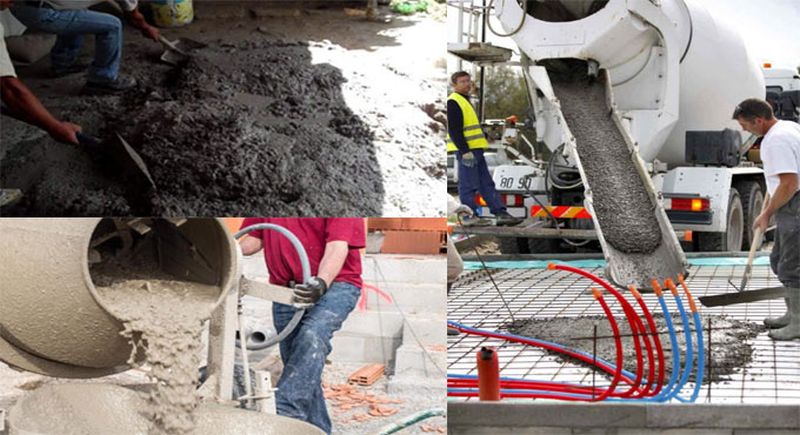

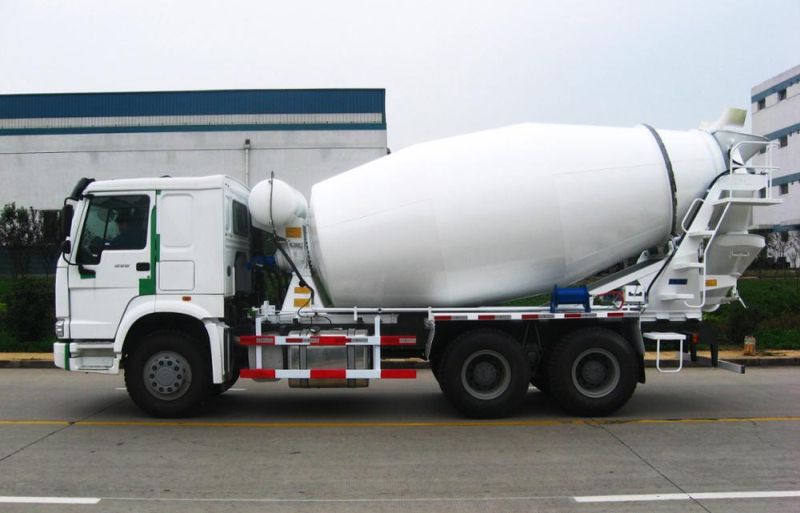
3. TRANSPORTING
Concrete can be moved using a variety of techniques and equipment. The precaution to be taken when transporting concrete is to retain the homogeneity established during mixing while being carried to the final deposition location.
The methods adopted for the transportation of concrete are:
- Mortar Pan
- Wheel Barrow, Hand Cart
- Crane, Bucket and Ropeway
- Truck Mixer and Dumpers
- Belt Conveyors
- Chute
- Skip and Hoist
- Transit Mixer
- Pump and Pipe Line

4. PLACING CONCRETE
It is not enough to have a well designed, batched, mixed, and delivered concrete mix; it is also critical that the concrete be put in a methodical manner to achieve the best outcomes.
The precautions to be taken and the strategies to be used when putting concrete in the conditions below will be described.
- Pouring concrete into a mould made of dirt. (For instance, foundation concrete for a wall or a column.)
- Pouring concrete into a big earth mould or a piece of wood formwork. (For instance, a road slab or an airfield slab.)
- Adding layers of concrete to wooden or steel shutters. (For example, mass concrete in dam construction or concrete abutment or pier construction).
- Placing concrete within the confines of normal work. (For instance, columns, beams, and floors)
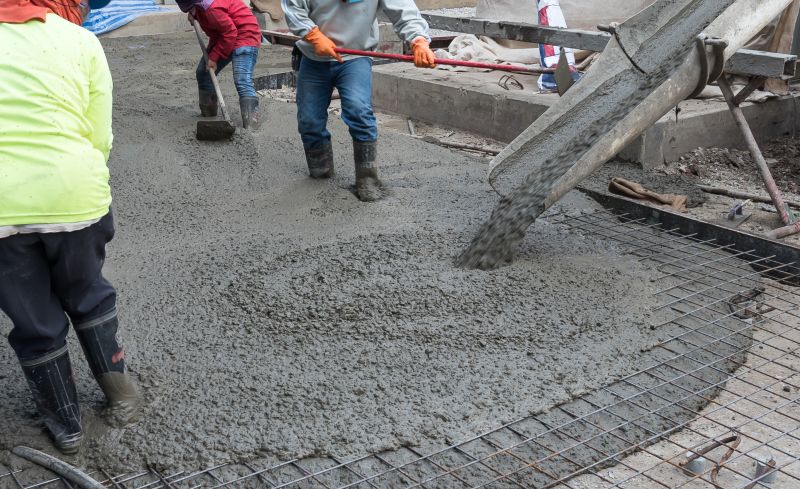

5. COMPACTING
Definition : Compaction of concrete is the process adopted for expelling the entrapped air from the concrete so as to make the concrete dense. In the process of mixing, transporting and placing of concrete air is likely to get entrapped in the concrete. The lower the workability, higher is the amount of air entrapped. In other words, stiff concrete mix has high percentage of entrapped air and, therefore , would need higher compacting efforts than high workable mixes. If this air is not removed fully, the concrete loses strength considerably. That is why its necessary to eliminate the voids.
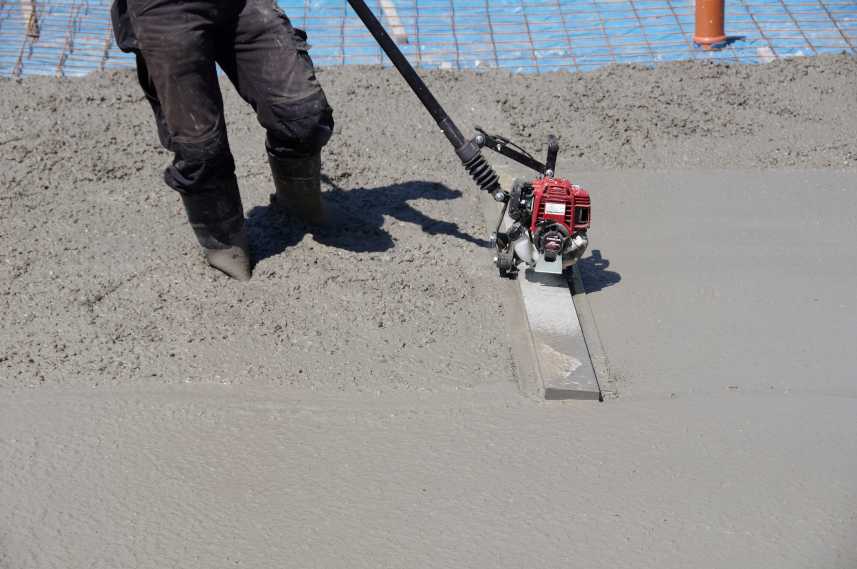

6. CONCRETE CURING
Curing is the process of keeping the concrete moist and warm enough to allow the cement to continue to hydrate.
More precisely, it is the process of maintaining a satisfactory moisture content and a favourable temperature in concrete during the period immediately following placement, so that cement hydration can continue until the desired properties have developed to a sufficient degree to meet the service requirement.
The quality of concrete will be poor if curing is neglected during the early stages of hydration.

