The slump test is the most popular way of determining concrete consistency, and it can be done in the lab or on the job site.
It is not good for extremely wet or extremely dry concrete. It does not account for all aspects that influence workability, nor is it always indicative of the concrete’s placability.
However, it is useful as a control test because it indicates the consistency of concrete from batch to batch.
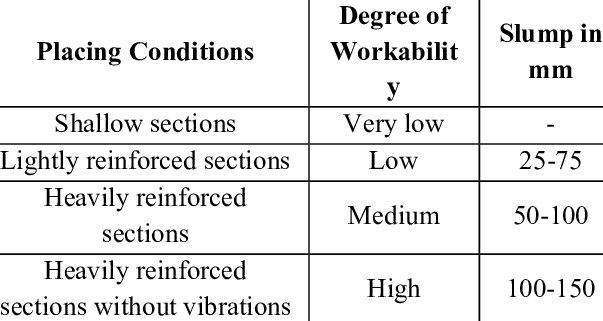
The slump test apparatus mainly consists of a metallic mould in the shape of a frustum of a cone with the internal dimensions as follows:
- 20 cm bottom diameter
- 10 cm top diameter
- 30 cm in height
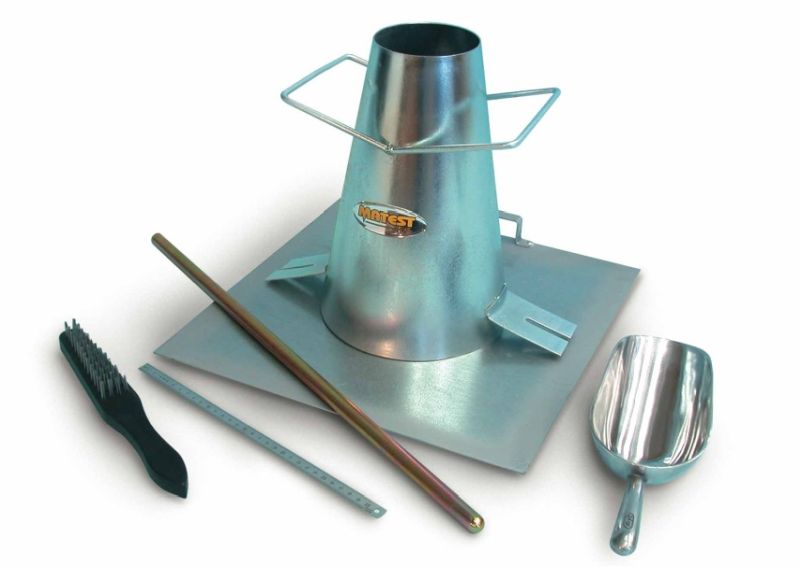

The copper sheet for the mould should not be thinner than 1.6 mm in thickness. Suitable guides for vertical lifting are sometimes included with the mould. A steel tamping rod with a bullet end and a diameter of 16 mm is used to tamp the concrete.
Before starting the test, the internal surface of the mould is completely cleaned and free of excess moisture and adherence of any old set concrete.
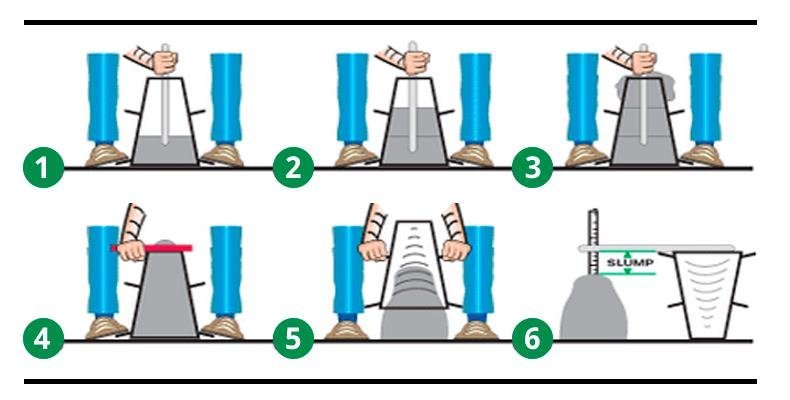
Slump test procedure:
- The mould is put on a non-absorbent, smooth, horizontal, solid surface.
- The mould is then filled in four stages, each about 1/4 of the way up the mold’s height.
- The tamping rod is used to tamp each layer 25 times, uniformly distributing the strokes across the cross section.
- The concrete is struck off level using a trowel and tamping rod after the top layer has been rodded. The mould is immediately removed from the concrete by slowly and carefully elevating it vertically.
- This permits the concrete to settle. Concrete SLUMP is the term for this type of subsidence.
- The level difference between the mold’s height and the highest point of the subsiding concrete is measured. Slump of Concrete is the variation in height in millimetres.
It is important to note that:
- True slump occurs when the concrete slumps evenly.
- Shear slump occurs when one half of a cone slides down.
- The difference in height between the height of the mould and the average value of the subsidence is used to calculate the slump value in a shear slump.
- Shear slump indicates that the concrete is non-cohesive and has segregation characteristics.
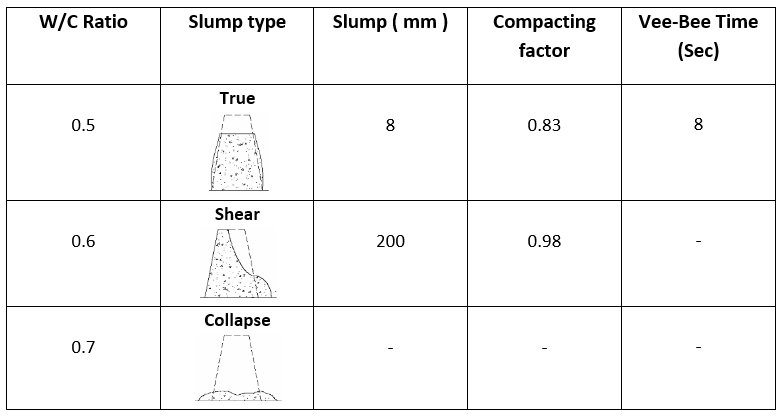
The slump test is suitable for slumps of medium to low workability, with slumps ranging from 5 to 260 mm. However, the test fails to distinguish between stiff mixes with zero slump and moist mixes with a collapse slump. It only applies to concrete with aggregates smaller than 38 mm (1.5 inch).