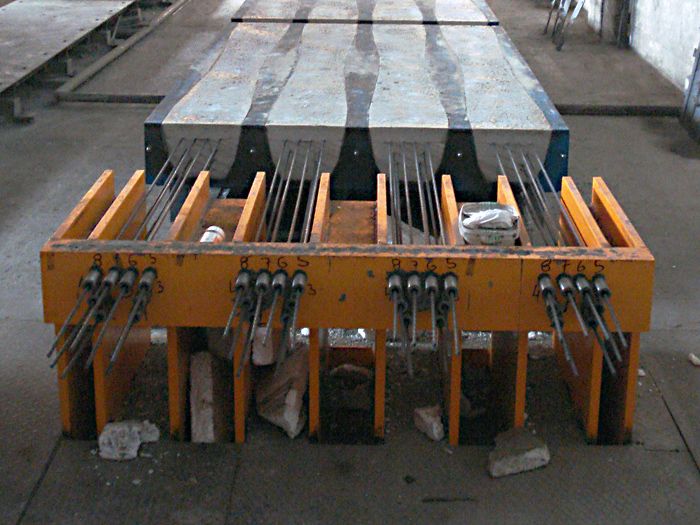
It is the deliberate application of a predefined compressive force in a structural member’s tension zone to overcome the concrete’s natural weakness in resisting tensile stress created owing to superimposed loads.
Prestressing is usually done using high-strength steel, which creates compressive stress, which causes the beam to bend upwards, balancing the downward deflection generated by superimposed loads. As a result, the member experiences minimal deflection and becomes uncracked over time.
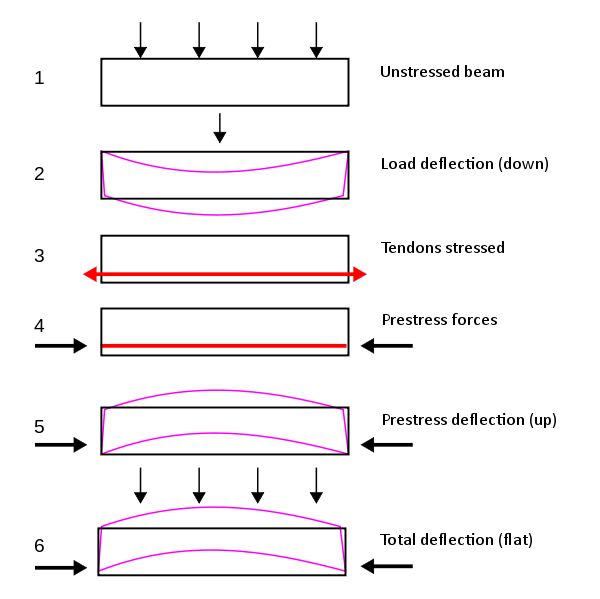
Benefits of PSC:
- Under service loads, the member’s cross-section stays uncracked.
- Corrosion of steel is decreased, resulting in increased durability.
- The member’s entire cross-section is used, which enhances the moment of inertia and stiffness, resulting in less deformation and increased serviceability.
- The member’s sheer resistance is raised.
- The PSC structures can be used in pressure vessels, liquid retention structures, and other applications.
- PSC structures are used for long span bridges because they have better performance under dynamic and fatigue loads.
- For the same time period, PSC members had a lower depth than RCC members, resulting in a lower death rate for PSC members. PSC members have lost weight, are more attractive due to their slim sections, and are the most cost-effective.
PSC’s Limitations:
- Because PSC is more technologically savvy than RCC, it is less common.
- Equipment that is relatively more expensive and costly.
- The initial investment is substantial.
- Strict material quality control is a must.
- It must be handled with care.
Pretensioning is analysed:
In the analysis, the following assumptions are made:
- Plan section persists even after bending since concrete is a homogeneous and elastic material.
- Hooks law is applied.
- Both under tension and compression, the material has the same properties.
- Initially, all members are straight.
Concentric prestressing:
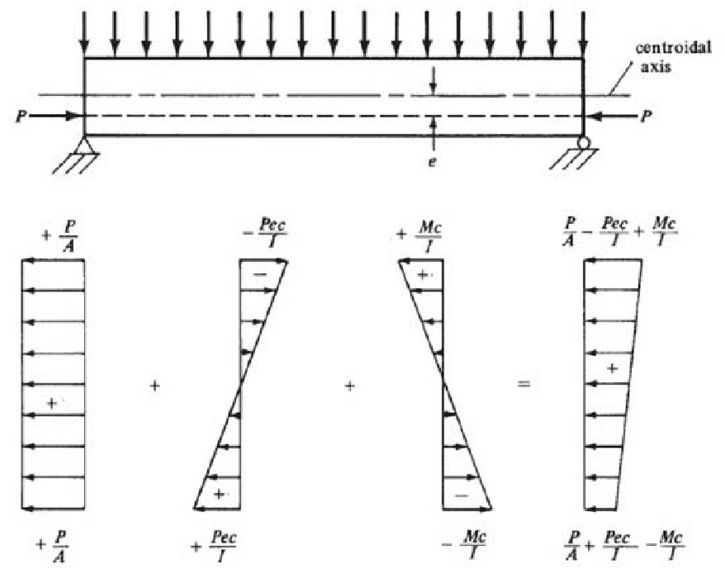
In concentric prestressing tendon passes through the centroid of the cross-section of the members only direct compressive stress is induced in the member due to the prestressing member along with bending stress due to dead and live load resultant stresses are obtained At the extreme fibers the stress distribution diagram are drawn due to prestressing force, dead load and live load.
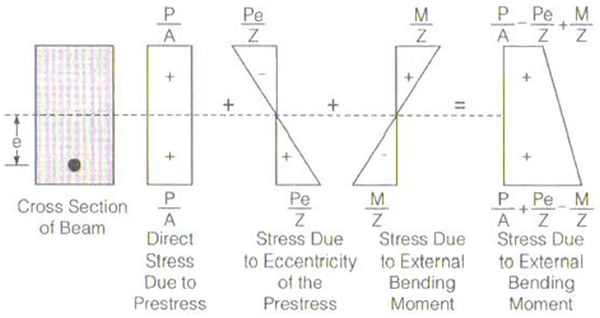
Eccentric prestressing:
Eccentric prestressing tendon is placed at an eccentricity “e” from the centroid of the section in the tension zone. Prestressing force “P” induces direct compressive stress and bending stress along with the bending stress due to dead load and live load resultant stresses are obtained at extreme fibre and stress distribution diagram are drawn due to the prestressing force, dead load and live load.