The variable types for input and output must always be defined using format specifiers, and the output must always be formatted using escape characters when writing a programme in C.
Format Specifiers
- In C programming, the type of data we are writing to the output or accepting through the input is specified by a format specifier. When using scanf() or printf, we can use this to inform the compiler what kind of variable we are using for input (). Format specifiers include %d, %c, %f, etc. as examples.
Here is a list of almost all format specifiers.
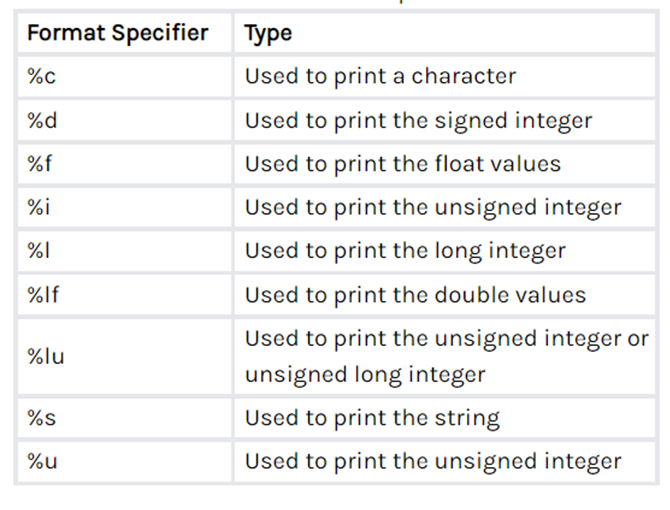
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char c[100] = "studentproject";
printf("Printing a string, %s.", c);
}
Output: Printing a string,studentproject.
A format specifier, the%s is utilised in the printf() function. This format specifier instructs printf() to treat it as a string and print the appropriate information.
Escape sequences
- The idea of escape sequences is supported by several computer languages. A string of characters known as an escape sequence is used to format the output. While printing, they are not visible on the screen. Each character serves a distinct purpose. For instance, the letters t and n are used to add a tab and a new line, respectively.
Here is a list of every escape Sequences.
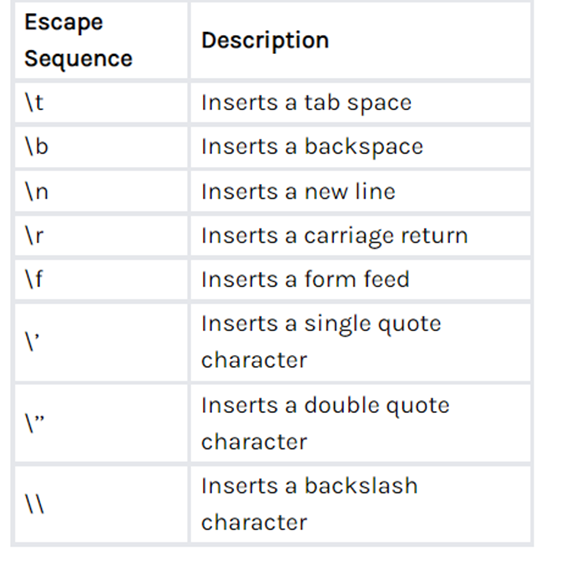
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("Printing inside a double quotation, \"student project\"");
}
Output: Printing inside a double quotation, “studentproject”.
